This tutorial will demonstrate how to implement the One-to-Many Mapping in your Spring Boot application that uses Hibernate/Spring Data JPA. As a database, I will use a MySQL server.
If you are learning about Hibernate, you might also be interested in the following tutorials:
- One-to-One Mapping Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot and MySQL
- Many-to-Many Relationship in Spring Boot Rest +JPA
- Show Hibernate SQL Query in Spring Boot
To demonstrate how the one-to-many relationship works, I will implement two JPA entities: a Book and a Story. One book can have many stories, and many stories can be associated with one book. This relationship is called “one-to-many”.
Before going ahead, let’s see some points.
We will implement two JPA entities: Book.java and Story.java. The Book and the Story entity will have One to Many and Many to One Bidirectional.
For this example, I am assuming One book can have many stories, and many stories can be associated with one book. I will use two annotations in my code to make it work: @OneToMany and @ManyToOne annotations.
When it comes to database tables, then we will not be creating any database tables ourselves. Because I will use Spring Data JPA, all database tables will be created by the framework based on how the JPA entity is annotated. So pay special attention to the annotations used.
Default Fetch Types
We will use two special annotations to implement the one-to-many relationship:
- @OneToMany and
- @ManyToOne.
These and other similar annotations have a default fetch type. I feel it is useful to mention their default values here.
- @OneToOne – The default fetch type is EAGER.
- @OneToMany – The default fetch type is LAZY.
- @ManyToOne – The default fetch type is EAGER.
- @ManyToMany – The default fetch type is LAZY.
You will use:
- Spring Boot,
- Maven,
- Embedded Tomcat,
- Postman,
- Eclipse and,
- MySQL database.
One-to-Many Mapping in Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot
Create a new maven project, open pom.xml, and replace it with the code below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.3</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.onetoonehibernatejpa</groupId>
<artifactId>onetoone</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>onetoone</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Let maven download all necessary jars. Once it is done, you will be able to see the maven dependency folder, which contains different jar files. You can start writing our controller classes, ServiceImpl and Repository. The directory structure of the application looks as below.
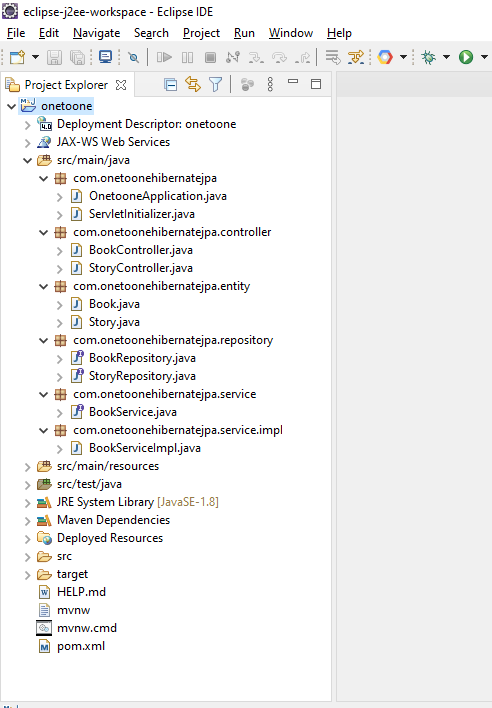
The Book JPA Entity
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@Entity
@Table(name = "book")
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int bookId;
@Column(name = "book_name")
private String bookName;
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.EAGER, mappedBy = "book", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JsonIgnoreProperties("book")
private List<Story> storyList = new ArrayList<>();
public int getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(int bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public List<Story> getStoryList() {
return storyList;
}
public void setStoryList(List<Story> storyList) {
this.storyList = storyList;
}
}
The Story JPA Entity
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@Entity
@Table(name = "story")
public class Story {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int storyId;
@Column(name = "story_name")
private String storyName;
@ManyToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinColumn(name = "book_id", referencedColumnName = "bookId")
@JsonIgnoreProperties("storyList")
private Book book;
public int getStoryId() {
return storyId;
}
public void setStoryId(int storyId) {
this.storyId = storyId;
}
public String getStoryName() {
return storyName;
}
public void setStoryName(String storyName) {
this.storyName = storyName;
}
public Book getBook() {
return book;
}
public void setBook(Book book) {
this.book = book;
}
}
Define a Repository Interface Extending JpaRepository
The BookRepository
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity.Book;
@Repository
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book, String> {
public Book findByBookId(int bookId);
}
Define a Service interface
The BookService
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity.Book;
@Component
public interface BookService {
public Book saveBook(Book book);
public Book findByBookId(int bookId);
}
The StoryRepository JPA Repository
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity.Story;
@Repository
public interface StoryRepository extends JpaRepository<Story, String> {
}
Define Service Implementation Class
The BookServiceImpl Java Class
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.service.impl;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity.Book;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity.Story;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.repository.BookRepository;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.service.BookService;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
public Book saveBook(Book book) {
List<Story> storyList = new ArrayList<>();
// create first story
Story story1 = new Story();
story1.setStoryName("Arrays");
// create second story
Story story2 = new Story();
story2.setStoryName("Pointers");
// create third story
Story story3 = new Story();
story3.setStoryName("Loops");
// add all story into storyList. Till here we have prepared data for OneToMany
storyList.add(story1);
storyList.add(story2);
storyList.add(story3);
// Prepare data for ManyToOne
story1.setBook(book);
story2.setBook(book);
story3.setBook(book);
book.setStoryList(storyList);
book = bookRepository.save(book);
return book;
}
public Book findByBookId(int bookId) {
Book book = bookRepository.findByBookId(bookId);
return book;
}
}
The BookController
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity.Book;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.service.BookService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/book")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/savebook", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public Book saveBook(@RequestBody Book book) {
Book bookResponse = bookService.saveBook(book);
return bookResponse;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{bookId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Book getBookDetails(@PathVariable int bookId) {
Book bookResponse = bookService.findByBookId(bookId);
return bookResponse;
}
}
The StoryController.java
package com.onetoonehibernatejpa.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.entity.Story;
import com.onetoonehibernatejpa.repository.StoryRepository;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/story")
public class StoryController {
@Autowired
StoryRepository storyRepository;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/stories")
public List<Story> getBookDetails() {
List<Story> storyresponse = (List<Story>) storyRepository.findAll();
return storyresponse;
}
}
And finally, you have an application.properties file where you have database details.
application. properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test spring.datasource.username=test spring.datasource.password=test@123 spring.datasource.driver-class-name =com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #spring.jpa.show-sql: true
Let’s run our application and test the endpoints.
http://localhost:8080/book/savebook
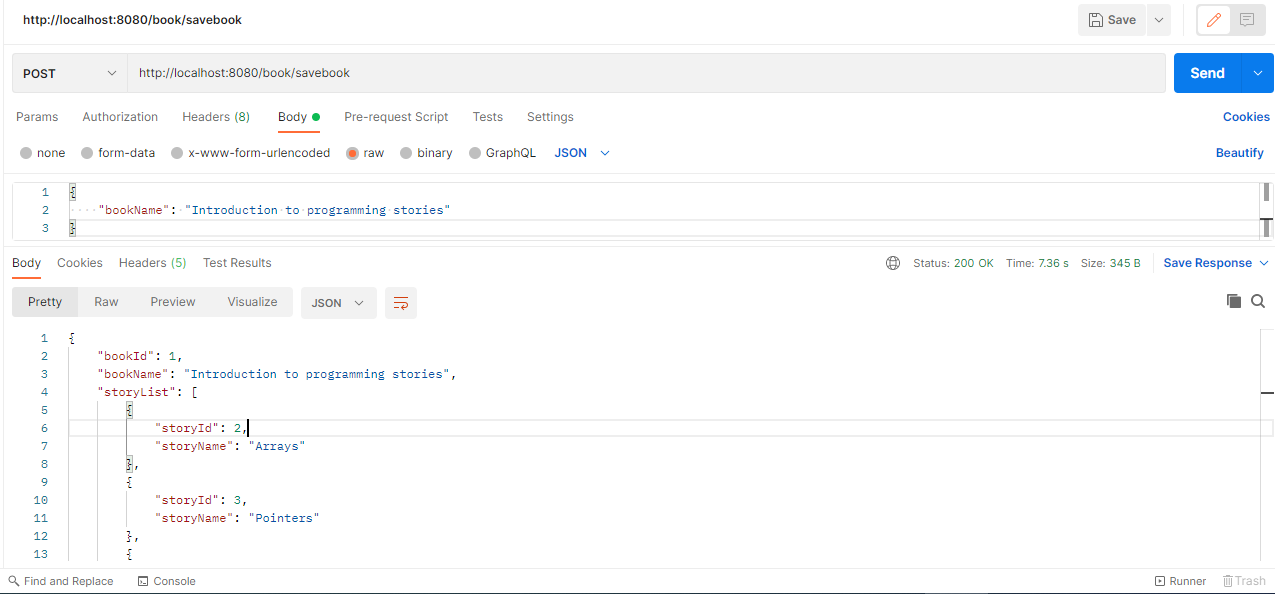
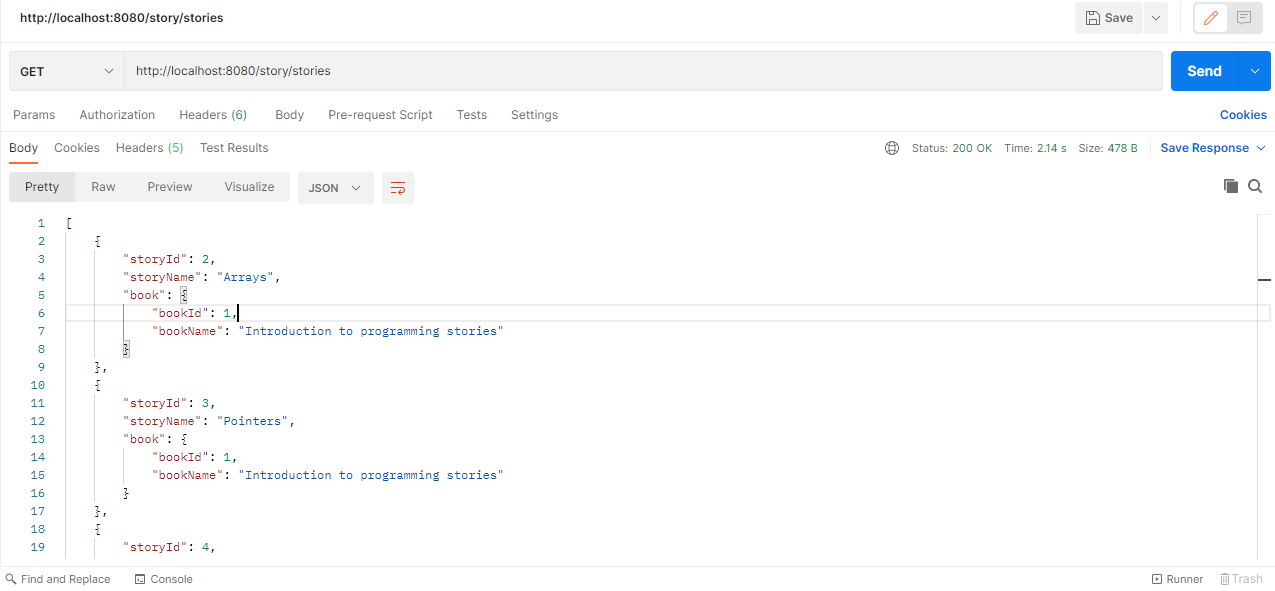
http://localhost:8080/story/stories
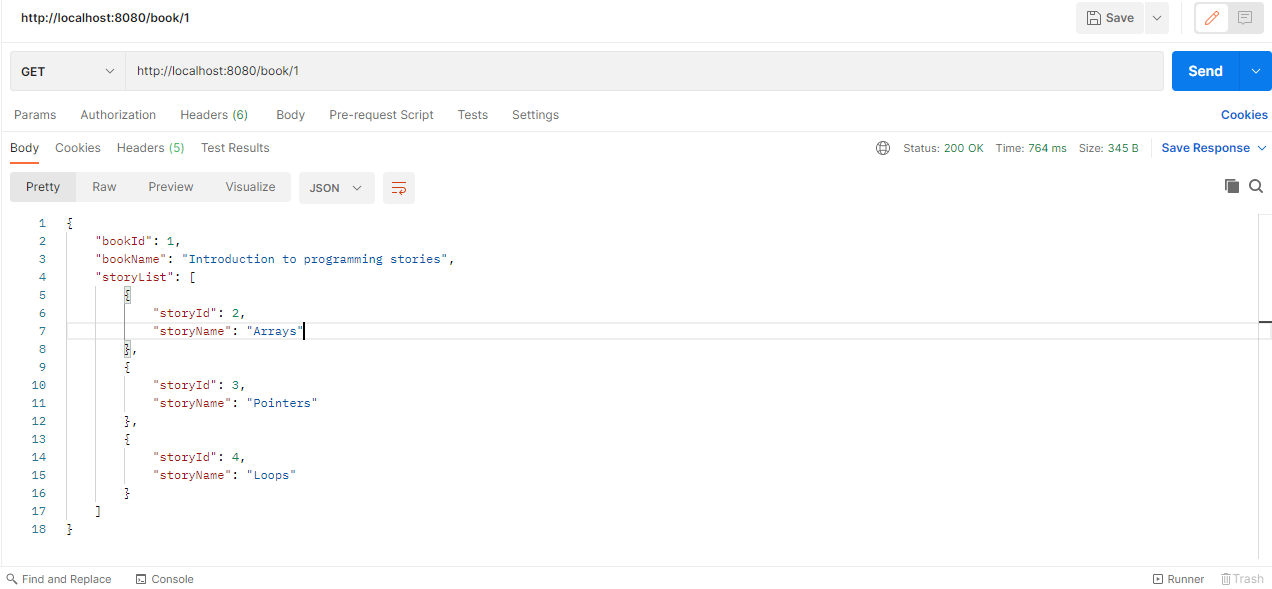
http://localhost:8080/book/1
Database details
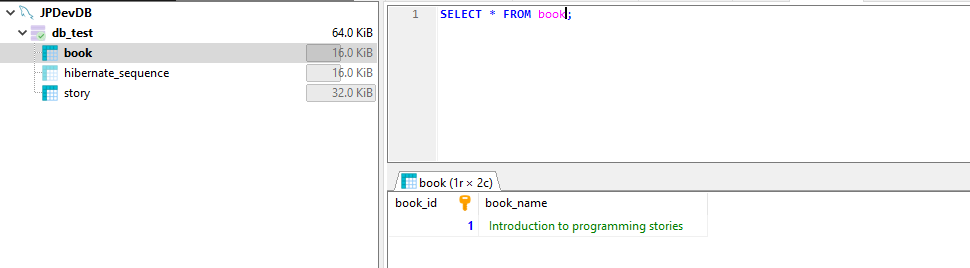
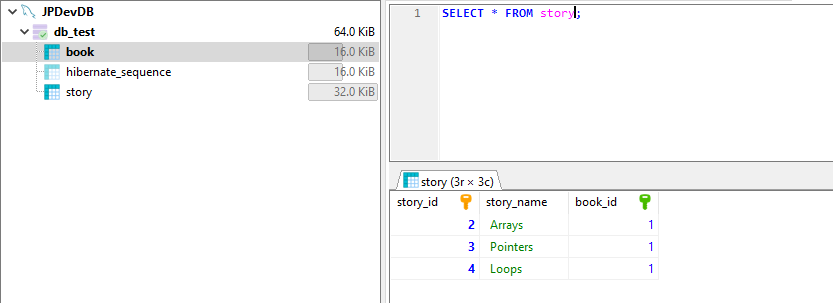
That’s about One-to-Many Mapping in Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot and MySQL.